 |
Complementary and Alternative Medicine, dubbed “CAM” by the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health, refers to treatments that are not part of traditional medical practices. Although the terms “complementary” and “alternative” are often used interchangeably, there are several significant differences between the two.
Complementary treatments are used along with conventional medicine—as a “complement” to these treatments—hence the name “complementary.” According to the Merck Manual Home Health Handbook, complementary treatments have been shown to help ease many of the symptoms associated with mesothelioma and asbestosis.
These treatments may also improve the quality of life of mesothelioma and asbestosis patients by lessening the side effects of conventional treatments such as chemotherapy and providing psychological and physical benefits.
Alternative treatments are often used instead of conventional treatments. Some of these therapies are unproven, and many claim to prevent, lessen, or even cure disease. Proven treatments are evidence-based, conventional, mainstream, or standard medical treatments that have been tested following a strict set of guidelines and found to be safe and effective.
Study results for proven treatments have been published in peer-reviewed journals and these treatments have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Still, the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM) says that in 2007, roughly 38 percent of U.S. adults aged 18 years and over and 12 percent of children used some form of CAM. This amounts to $33.9 billion—mostly out-of pocket. Further, more than 50 percent of cancer patients use some form of complementary and/or alternative medicine, spending more than $25 billion each year, and 80 percent of the world’s population uses herbal medicine—a complementary therapy.
Some of the most popular types of complementary therapies include:
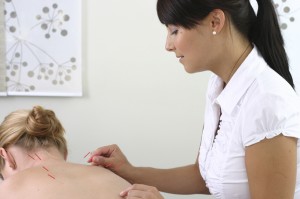
- Acupuncture – Acupuncture is the most widely accepted form of holistic medicine treatment during chemotherapy. Clinical studies show that this complementary therapy is effective in treating nausea caused by chemotherapy drugs and surgical anesthesia. This treatment tool is often a major component of mesothelioma treatment paths as well thanks to its ability to help reduce pain associated with the condition and its effectiveness in treating nausea.
- Aromatherapy – Early clinical trials suggest that aromatherapy may help reduce pain, stress, and depression when used as a complementary cancer treatment. In mesothelioma patients, essential oils may be used during massage to help the patient become more alert, yet relaxed, and mentally able to help fight the disease. The goal overall is to help enhance quality of life.
- Herbal Medicine – One in four drugs prescribed today are derived from plant sources. They are typically used in conjunction with conventional treatments (under a doctors care) to help treat everything from allergies to cancer (breast, lung, colon, mesothelioma) to chronic pain.
- Naturopathy – Naturopathic medicine combines many complementary approaches such as acupuncture, herbal medicine, aromatherapy and more to help manage and prevent symptoms.
- Reiki – According to the American Cancer Society (ACS), some conventional medical practitioners report that reiki, a treatment that manipulates energy fields within and around the body to release the body’s natural healing powers, may be useful as a complementary therapy to help reduce stress and improve quality of life for those afflicted with asbestosis, mesothelioma, and other types of cancer. Reiki may also help reduce muscle fatigue in cancer patients.
Popular alternative treatments include natural products such as fish oil and garlic, which enhance health and promote wellness, as well as:
- Deep Breathing – May help relieve stress and anxiety, and promotes relaxation in mesothelioma patients.
- Diet/Nutrition Therapy – Typically recommended to help lower the risk of disease, such as cancer. The ACS offers several diet-based recommendations to help reduce cancer risk. You should choose most of the foods you eat from plant sources (eat five or more servings of fruits and vegetables every day), limit fat intake—especially from animal sources, and limit or eliminate alcohol intake.
Diet/nutrition therapy may also help mesothelioma patients maintain strength and decrease side effects and recovery time from radiation, chemotherapy and other chemical/drug treatments.
- Guided Imagery – May help ease the side effects of chemotherapy in mesothelioma patients and other cancer patients. May also help with pain management, stress and anxiety reduction, depression, and high blood pressure. Guided imagery may create feelings of being in control.
- Homeopathic Treatment – Researchers suggest that these treatments have a placebo effect, which results in feelings of increased hope and optimism, based on the feeling that the therapy is actually working.
- Massage – Helps decrease stress, anxiety, depression, and pain. Massage increases alertness on its own and when used with essential oils.
- Meditation – May induce changes in the body, such as the body’s “fight-or-flight” response, and may help relieve stress and anxiety.
- Progressive Relaxation – May reduce signs and symptoms of illness such as pain, headaches, and nausea. It may also reduce blood pressure, increase blood flow to major muscles, slow heart and breathing rate, lessen muscle tension, improve concentration, and give you more energy.
- Yoga – May relieve symptoms associated with chronic diseases such as asbestosis, mesothelioma, and other types of cancer as well as arthritis and heart disease. Also promotes relaxation and increases physical fitness in patients.
Each individual patient is different, so treatment paths are rarely one size fits all. Today, doctors are even delving deeper into the world of integrative medicine, which “combines the best of today’s high-tech medicine with the best of non-traditional practices,” says the Mayo Clinic Book of Alternative Medicine. The goal of integrative medicine is to treat the disease and the whole person—mind, body, and spirit.
For example, at Cancer Treatment Centers of America (CTCA), an integrative medicine program is often employed to help treat the “whole” mesothelioma patient.
An integrative medicine program such as CTCA’s may combine elements of nutrition therapy, naturopathic medicine, pain management, mind-body medicine, spiritual support, and oncology rehabilitation to be used in conjunction with conventional treatments.
For more information about complementary and alternative treatments, request a free copy of 100 Questions & Answers About Mesothelioma here or contact the client services team at MRHFM by calling 1-866-373-5000.
Sources
American Cancer Society’s Guide to Complementary and Alternative Cancer Methods
Print. Foreword by David S. Rosenthal, MD
Cancer Treatment Centers of America (CTCA)
Mayo Clinic Book of Alternative Medicine
Print. Brent Bauer, MD., Medical Editor
National Cancer Institute and the National Institutes of Health (NCI NIH)
NIH National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM)
The Merck Manual Home Health Handbook
Print. Robert S. Porter, MD., Editor-in-Chief


No comments yet. You should be kind and add one!
By submitting a comment you grant Mesothelioma Blog – Information, Research, News, Answers, Legal a perpetual license to reproduce your words and name/web site in attribution. Inappropriate and irrelevant comments will be removed at an admin’s discretion. Your email is used for verification purposes only, it will never be shared.